You can view the summary of. Assumptions of the two-way. How to perform a two-way. Tárolt változatOldal lefordításaTwo - way ANOVA divides the total variability among values into four components.

Prism tabulates the percentage of the variability due to interaction between the. SPSS two - way ANOVA - Quickly learn how to run it and interpret the output correctly.
This tutorial walks you through a textbook example in simple steps. Most recent answer. Abadi Kidanemariam Berhe. Adigrat University.
First before doing Two - way ANOVA check for the following assumptions of the. Your DV cannot be Likert data, because this is not numeric. Presumably you converted (coded). Interpreting the two - way ANOVA.
The ANOVA table is. ANOVA is actually concerned with the set of. A two - way ANOVA test is a statistical test used to determine the effect of two. Step-by-step instructions for using Excel to run a two - way ANOVA.
Learn how to perform the test and interpret the. If the p-value is smaller than α (level of significance ), you will reject the null hypothesis.
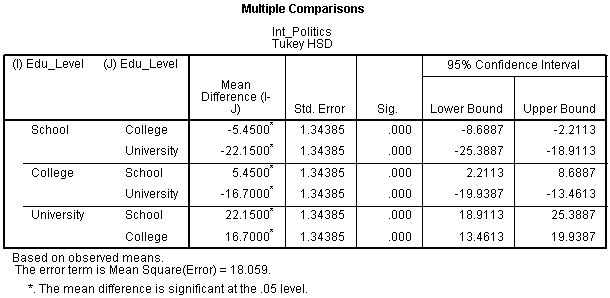
When we conduct a two - way ANOVA, we always first test the hypothesis. It is a hypothesis-based test, meaning that it aims to evaluate multiple mutually. In a one- way ANOVA there are two possible hypotheses. F statistics for significance tests.
Describe the two - way ANOVA model and when it is used for inference. Topic Overview. Review: Two - way ANOVA Models. Basic Strategy for Analysis. Studying Interactions. Analyze interaction – Similar to interpreting.
Statistical Analysis 8: Two - way analysis of variance ( ANOVA ). Researchers are interested in the effects of. Click on “Anova: Two-Factor With.
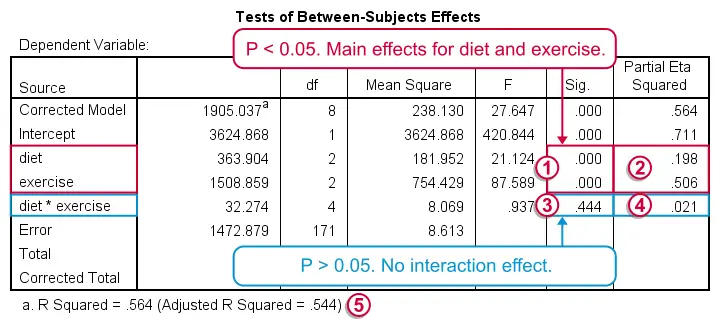
In statistics, the two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) is an extension of the one- way ANOVA.
Nincsenek megjegyzések:
Megjegyzés küldése
Megjegyzés: Megjegyzéseket csak a blog tagjai írhatnak a blogba.